What equipment can detect partial discharge?
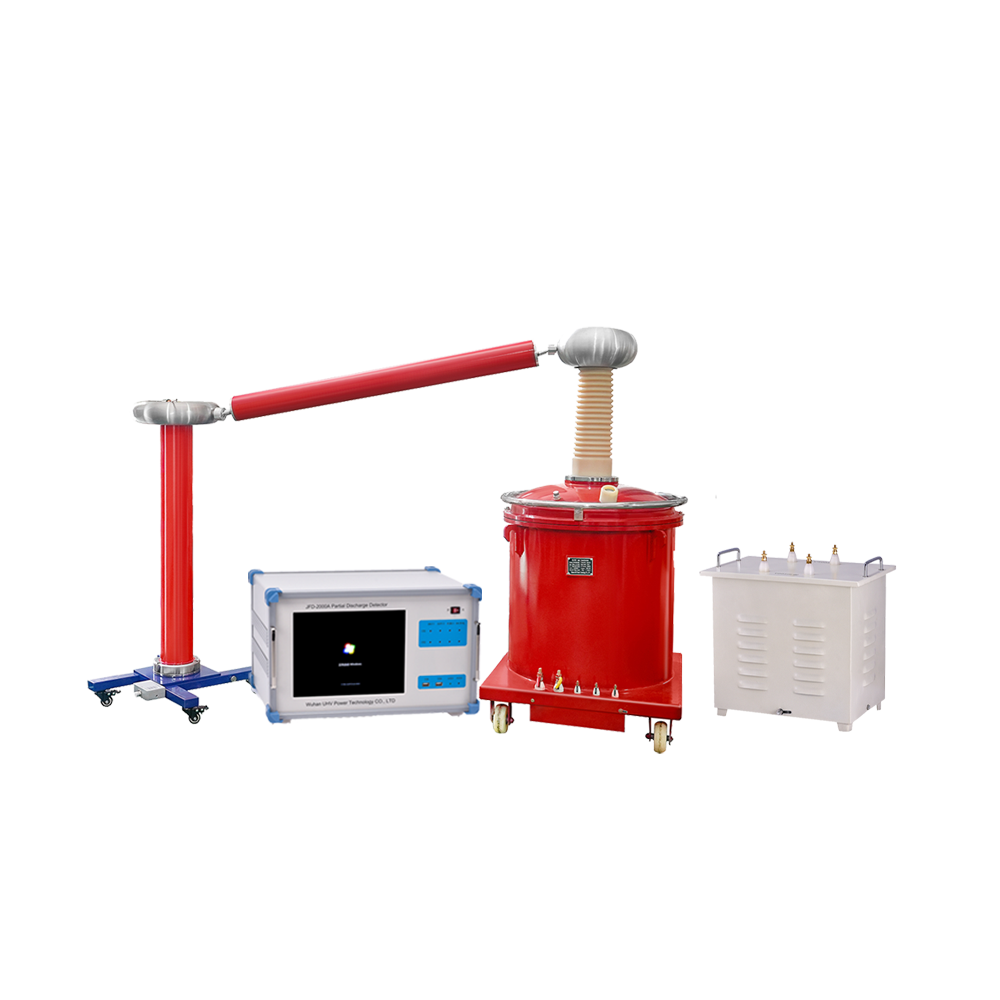
Let's analyzePartial Discharge Testers– instruments specifically designed to capture, measure, and analyze partial discharge phenomena occurring within electrical equipment. Based on detection principles and application scenarios, the main types are:
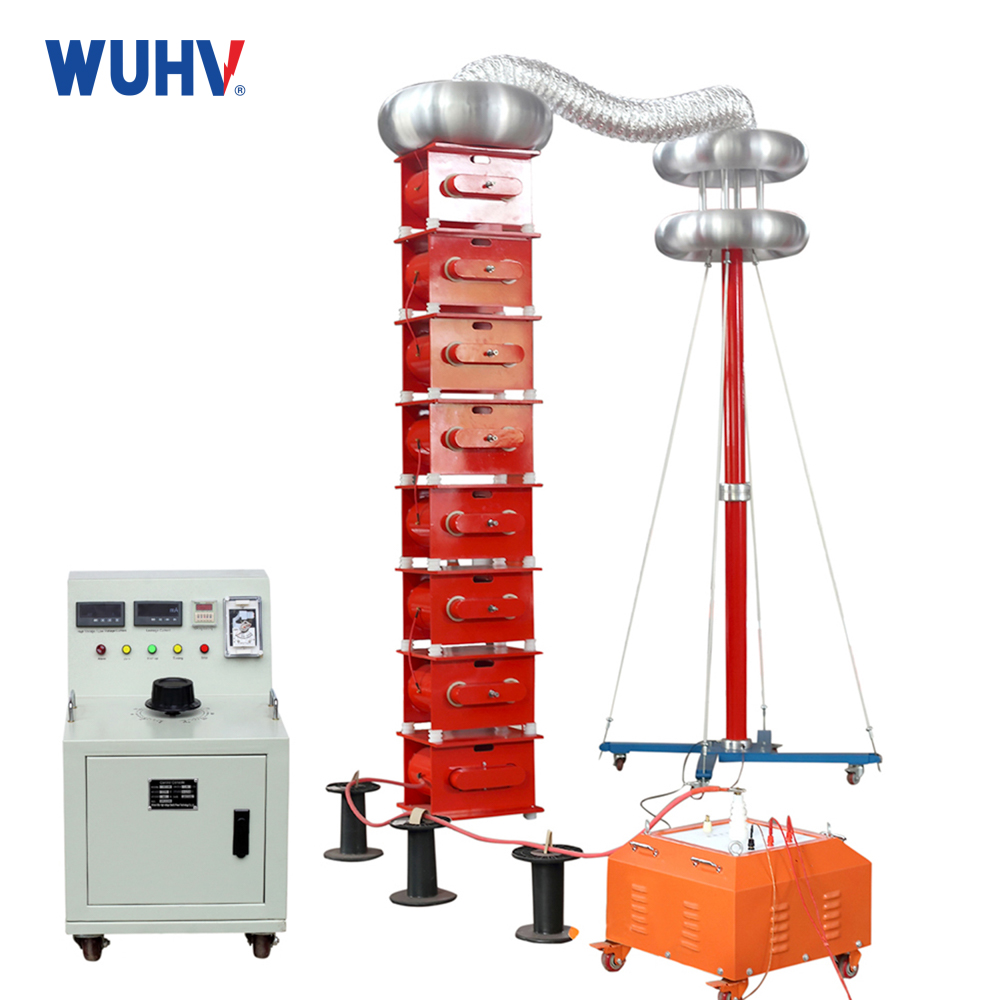
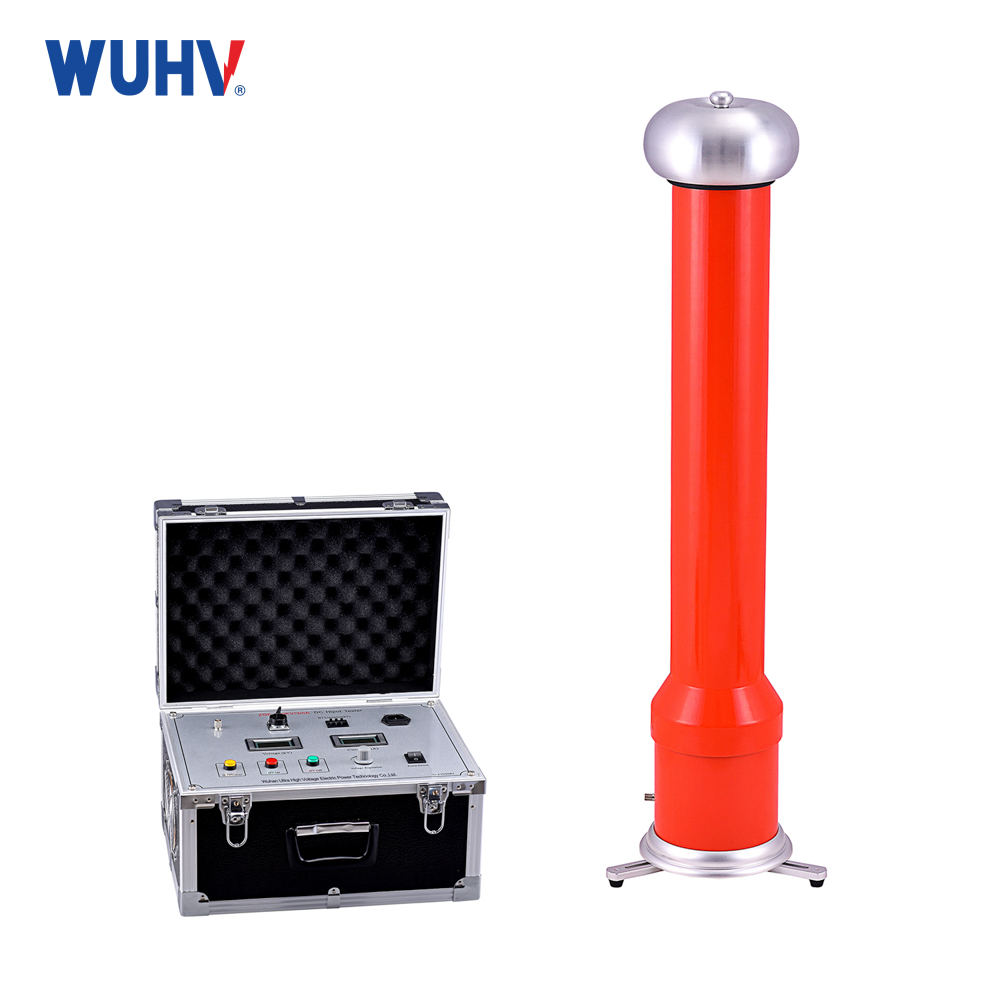
1.Pulse Current (IEC 60270):
Measures: Current pulses in ground connection.
Pros: Most accurate quantification (pC).
Cons: Needs direct connection, often offline, sensitive to noise.
Use: Lab/factory tests, critical offline diagnostics (transformers, cables).
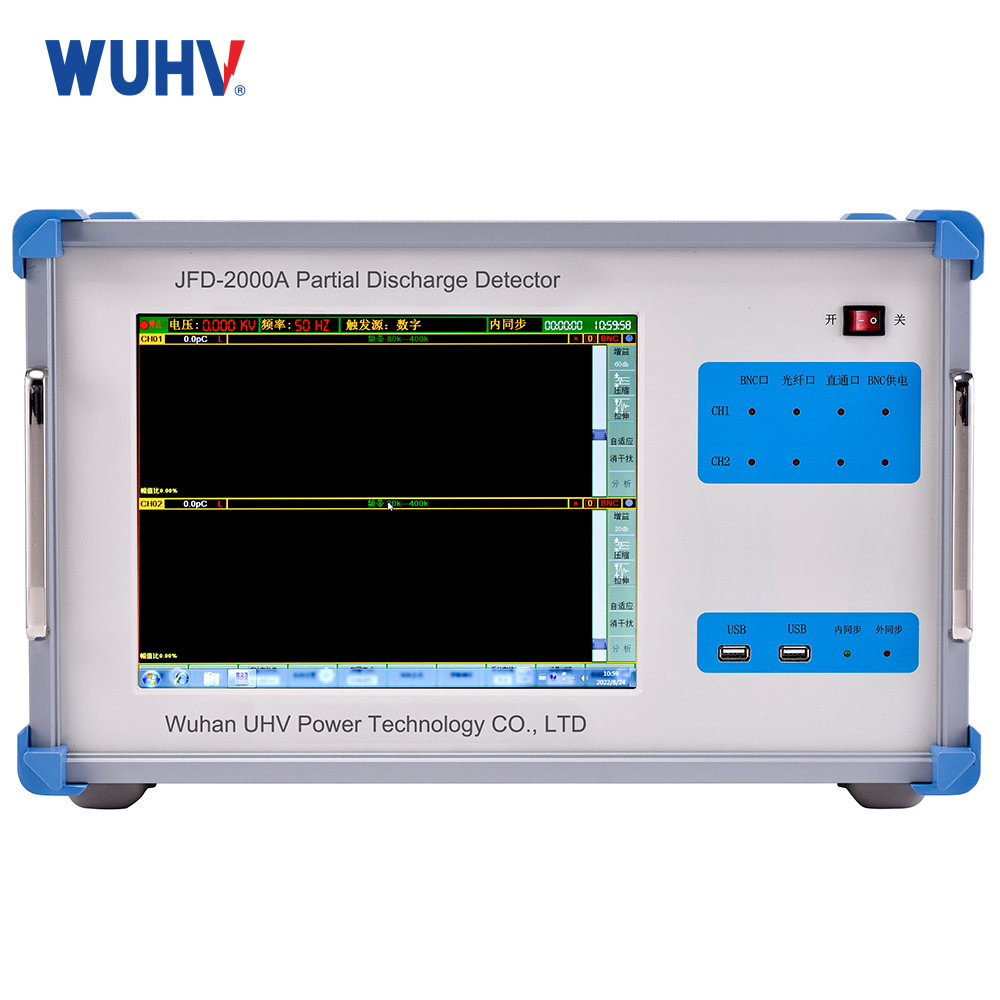
2.Ultra-High Frequency (UHF):
Measures: Radio waves (300MHz-3GHz) from PD.
Pros: Non-contact, good noise immunity, online capable.
Cons: Hard to calibrate (pC), complex signal paths.
Use: Online monitoring (GIS/GIL), transformers, switchgear.
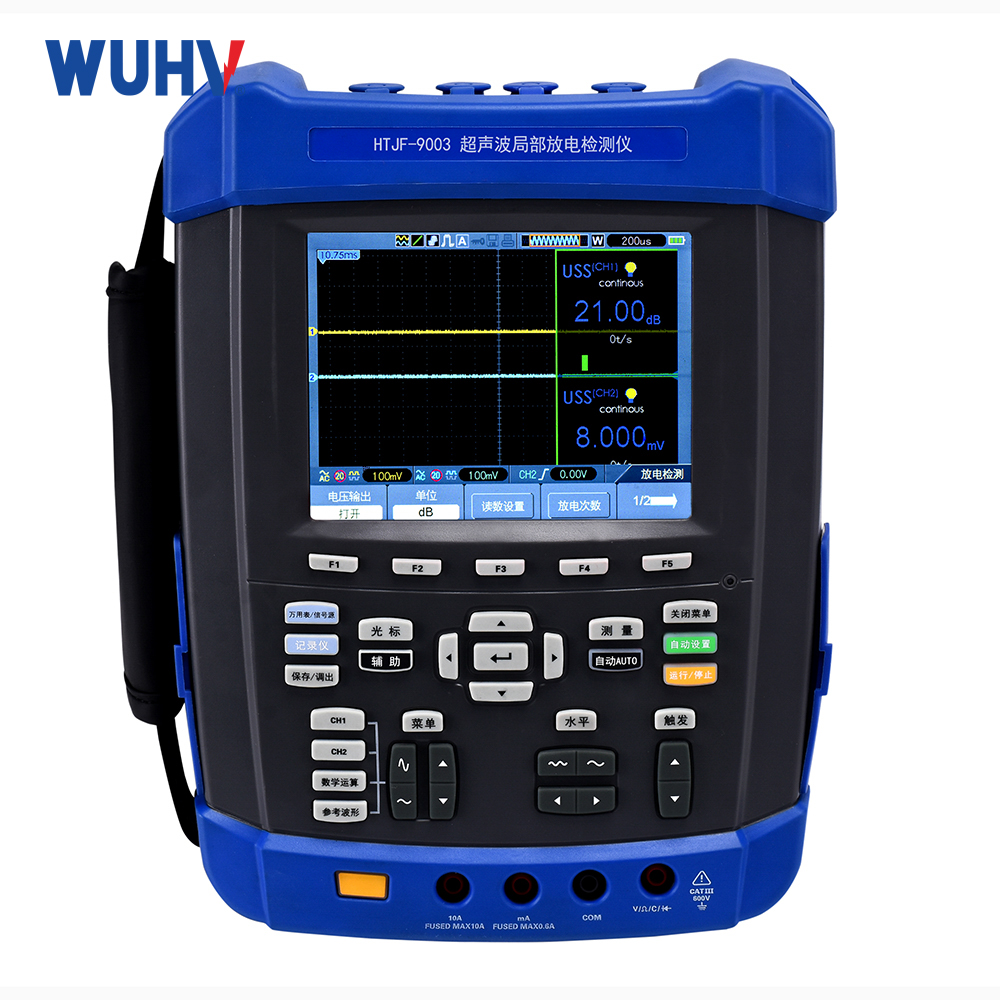
3.Ultrasonic (Acoustic):
Measures: Sound waves (20kHz-300kHz) from PD.
Pros: Pinpoints location, immune to electrical noise, online capable.
Cons: Hard to quantify (pC), signal weakens through material.
Use: Locating PD sources live (transformers, switchgear, cables).
4.Transient Earth Voltage (TEV):
Measures: Voltage pulses on metal surfaces (dBµV).
Pros: Very fast, simple, cheap, online for switchgear.
Cons: Lower sensitivity, surface only, prone to interference.
Use: Quick screening of MV switchgear/RMUs.
Key Points:
No single best type: Choose based on equipment, need (quantify/locate/online), and environment.
Modern detectors often combine methods (e.g., UHF + Ultrasound) for better results.
Core function: Detect weak PD signals reliably amidst noise.